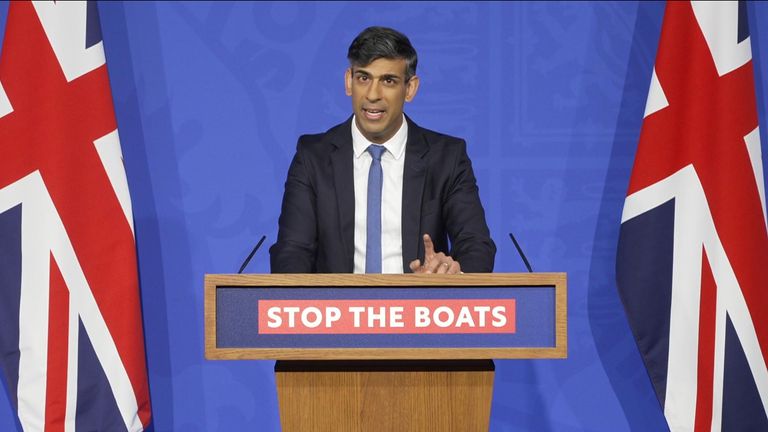
After months of delay, parliamentary bickering and legal challenges, Rishi Sunak’s Rwanda bill is set to become law.
Legislation for the prime minister’s controversial plan to deport asylum seekers to the landlocked African country cleared parliament last night after a lengthy battle.
The policy has been plagued by setbacks since it was first announced two years ago, with thousands of people arriving on Kent beaches aboard small boats all the while.
So what is the Rwanda bill and why is it so controversial? Here are some of the key questions, answered.
What is the Rwanda asylum plan?
Rishi Sunak’s promise to “stop the boats” is one of five pledges he has staked his premiership on.
Key to this is the Rwanda scheme, which would involve some asylum seekers being sent to Rwanda to have their asylum claims processed there.
If successful, they can be allowed to stay in Rwanda or seek asylum in another country. But they would not be able to apply to return to the UK.
Ministers say the policy will act as a deterrent to people thinking of travelling to the UK “illegally” (though whether or not crossing the English Channel in a small boat is actually illegal is complicated).
Why haven’t any planes taken off already?
The first plane carrying asylum seekers could take off in 10 to 12 weeks, the prime minister said ahead of the law passing, in what is another delay, having initially promised this would happen in the spring.
This would be more than two years since the first flight attempted under the deal was grounded amid last-minute legal challenges.
No asylum seekers have yet been sent to Rwanda.
While he refused to go into “sensitive” operations details on Monday, Mr Sunak did outline a number of measures the government was taking to prepare for the first flights to take off.
He said there were now 2,200 detention spaces and that 200 dedicated caseworkers had been trained to process claims quickly.
Around 25 courtrooms have been made available and 150 judges will provide 5,000 sitting days, he added.
Mr Sunak also said there were 500 “highly trained individuals ready to escort illegal migrants all the way to Rwanda, with 300 more trained in the coming week”.
In November, the Rwanda plan was ruled unlawful by the UK’s Supreme Court, which said those being sent to the country would be at “real risk” of being returned home, whether their grounds to claim asylum were justified or not – breaching international law.
Is Rwanda a safe country?
Much of the debate around the policy – putting aside differing views on whether it is effective or ethical – centres around the question of whether Rwanda is considered a “safe country”.
The government insists it is, although it’s worth pointing out that the UK granted asylum applications to 15 people from Rwanda last year.
According to Human Rights Watch, critics of the ruling political party in Rwanda have been “arrested, threatened, and put on trial”. Some said they were tortured in detention, the organisation added.
Who will be affected by the Rwanda scheme?
The Home Office plans to use the agreement with Rwanda to remove people who make dangerous journeys to the UK and are considered “inadmissible” to the UK’s asylum system – and will include people who have arrived irregularly since 20 July last year.
People whom the Home Office wishes to transfer to Rwanda will be identified and referred to the Rwandan authorities on a case-by-case basis, after an initial screening process following arrival in the UK, the government has said.
Although the agreement focuses on asylum seekers, under the treaty people who have made unauthorised journeys to the UK but not claimed asylum can be relocated to Rwanda as well.
Read more:
Analysis: Sunak staking premiership on Rwanda plan
How many asylum seekers does the UK remove?
What happened in parliament on Monday night?
On Monday, the Rwanda bill finally passed through the Commons and Lords and is now set to become law.
The legislation was introduced by the government in the wake of November’s Supreme Court ruling which had declared that Rwanda was not safe for refugees.
Since then, the government has signed a new treaty with Rwanda which it says contains additional safeguards for people relocated.
With the new bill, parliament was asked to declare that Rwanda must be treated as safe in order to render the relocation plan lawful in UK domestic law.
What happens now?
The bill is now headed for royal assent after passing through parliament, but it’s likely to still face various challenges.
Campaigners opposing the plans, and individual asylum seekers who are told they are to be sent to Rwanda, could look to take the government to court again in an attempt to stop flights.
Whether any legal challenges could be successful in light of the new law remains to be seen.
How much has this all cost?
A lot.
An investigation by Whitehall’s spending watchdog said the cost of the Rwanda scheme could rise to half a billion pounds, plus hundreds of thousands more for each person deported.
The government has refused to say how much more money, on top of the £290m already confirmed, that the UK had agreed to pay Rwanda under the deal. However, a National Audit Office report revealed millions more in spending including £11,000 for each asylum seeker’s plane ticket.
What are people opposed to the Rwanda asylum plan saying now the bill was passed?
The passing of the bill has sparked fresh condemnation from charities and other organisations.
Amnesty International said it will “leave a stain on this country’s moral reputation”.
Sacha Deshmukh, Amnesty International UK’s chief executive, added: “The bill is built on a deeply authoritarian notion attacking one of the most basic roles played by the courts – the ability to look at evidence, decide on the facts of a case and apply the law accordingly.
“It’s absurd that the courts are forced to treat Rwanda as a ‘safe country’ and forbidden from considering all evidence to the contrary.”